artificial plateau:building more site:
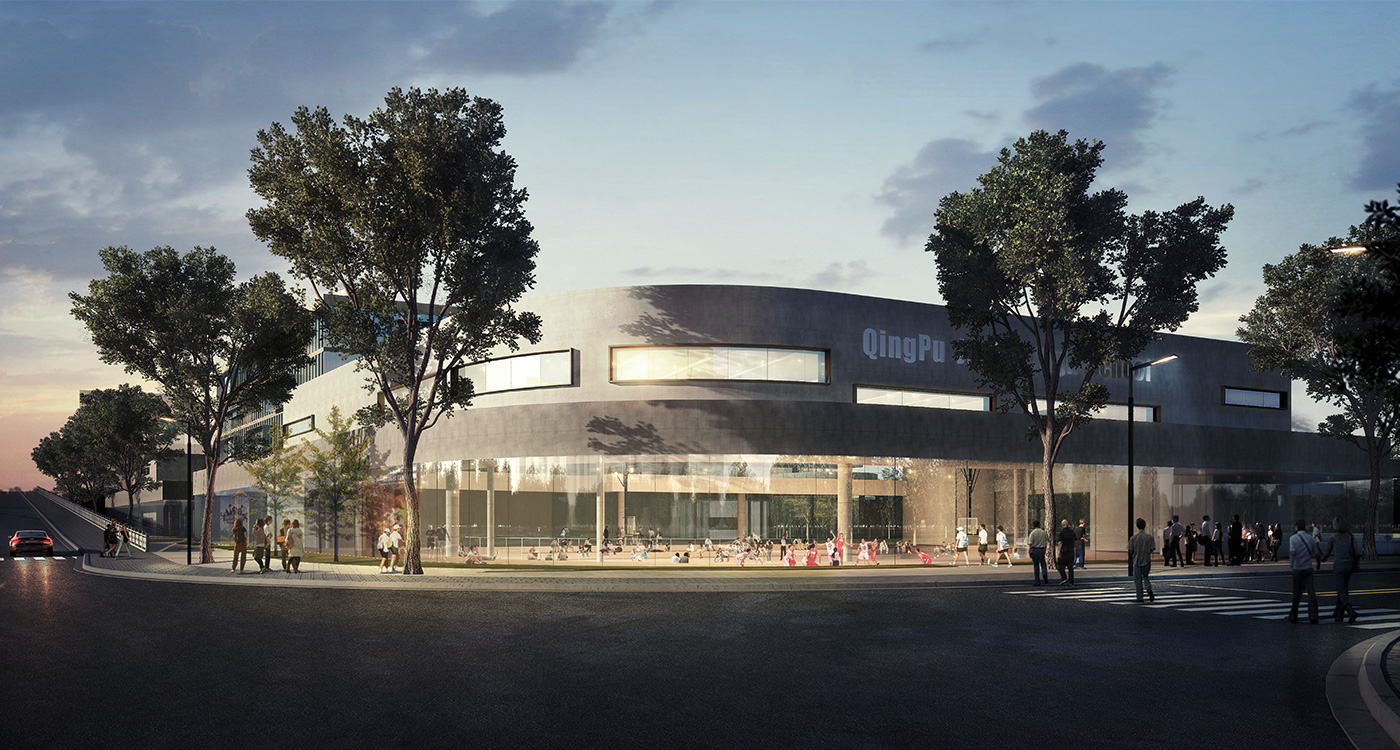
BAU599 Shanghai Qingpu Newtown 24-Class Junior High school
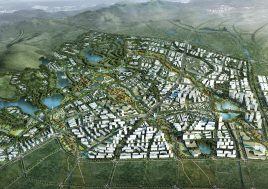
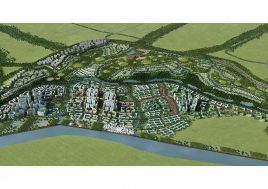
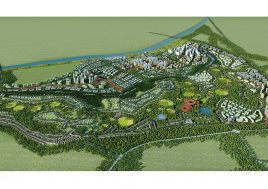
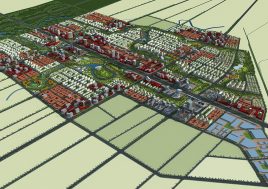
Qingpu District, Shanghai, China
Discipline
ArchitectureTypology
EducationCity
Qingpu District, Shanghai, ChinaDate
2017Status
Invited competition, Ongoing.Client
Shanghai Lake Dianshan Newtown Development Co., LtdProgram
24-class junior high schoolARTIFICIAL PLATEAU:
BUILDING MORE SITE:
Intro
China is building schools at an unprecedented rate countrywide. Limited land allocation, constrictive regulations, and an unbearable urgency are resulting in the mass production of traditional models. Ironically the education authorities and local governments are extremely open to new ideas. Now is the time for the latest in teaching-learning methodologies to be presented to and discussed with the authorities.
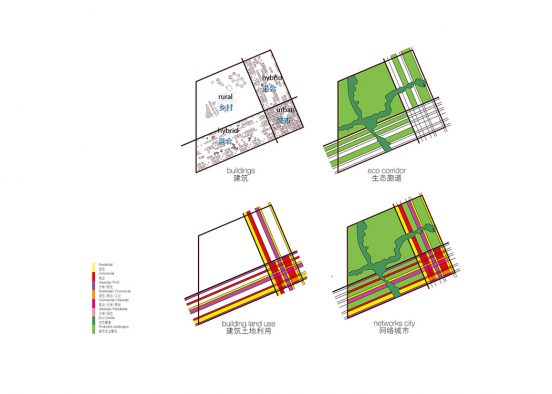
both and, not either or
In the West, education facilities are going through a major shift in their teaching and learning strategies and tactics. This shift is having profound effects on the spatial requirements of schools.
Like retail space and office space before it, these changes can often lead to radical swings from tried and true spatial solutions, to experimental ideas that are best summarized later as “…seemed like a good idea the time.” More often than not it is the complex middle ground, a mix of both the traditional solution and the more experimental ideas that offer the best solutions.
classrooms and the in-between
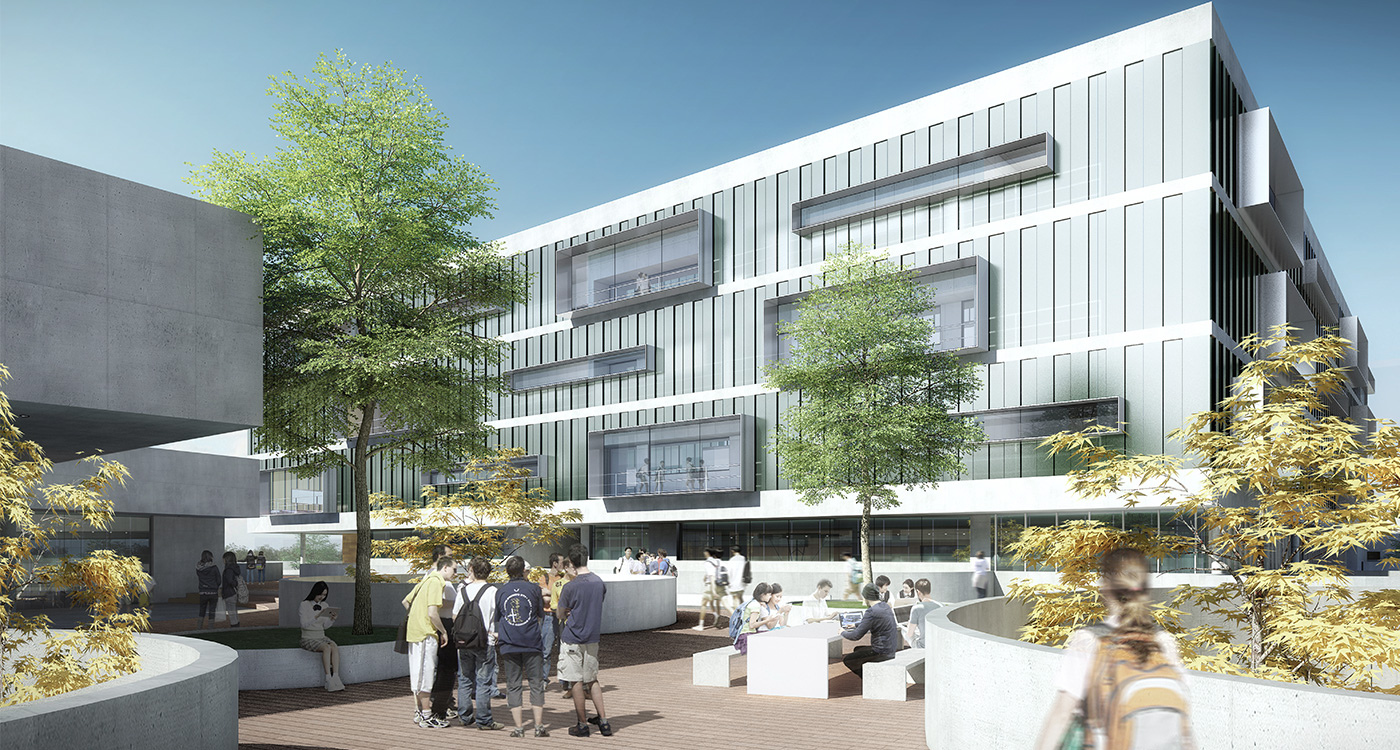
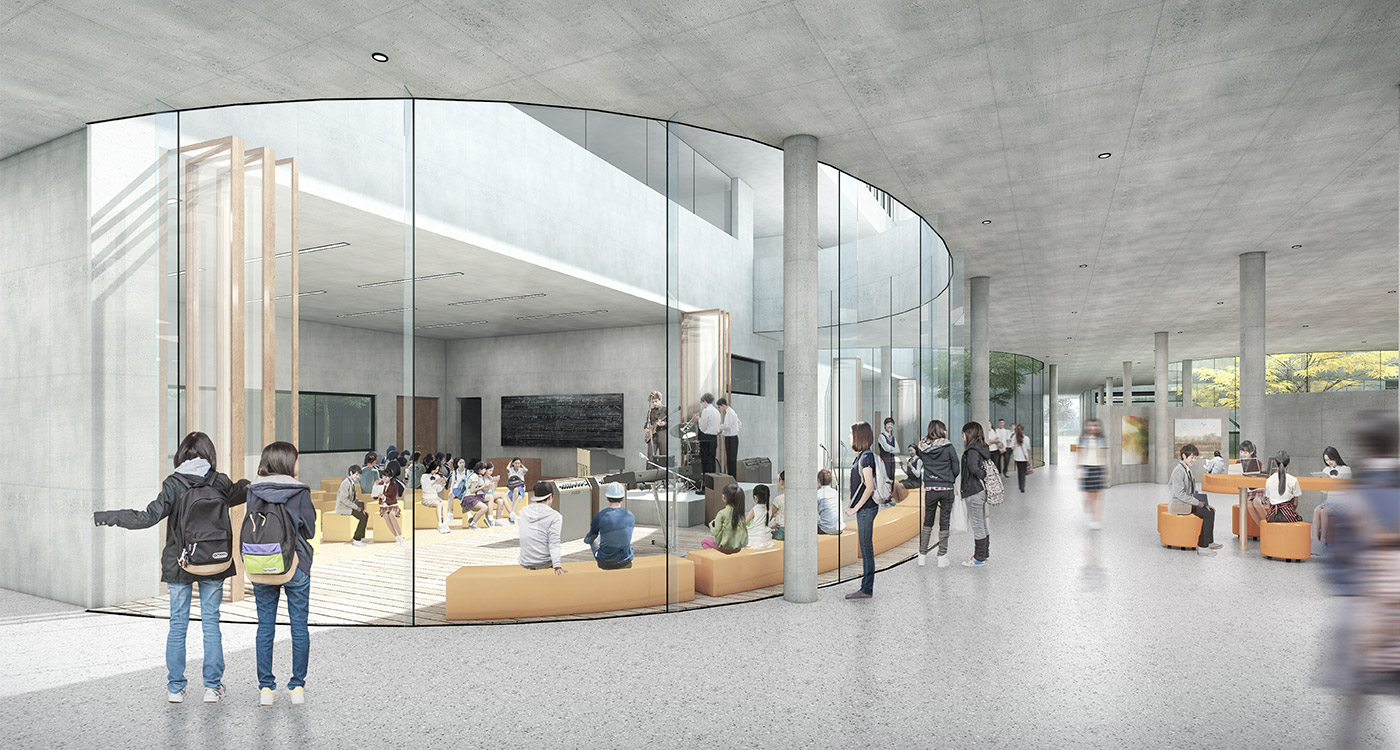
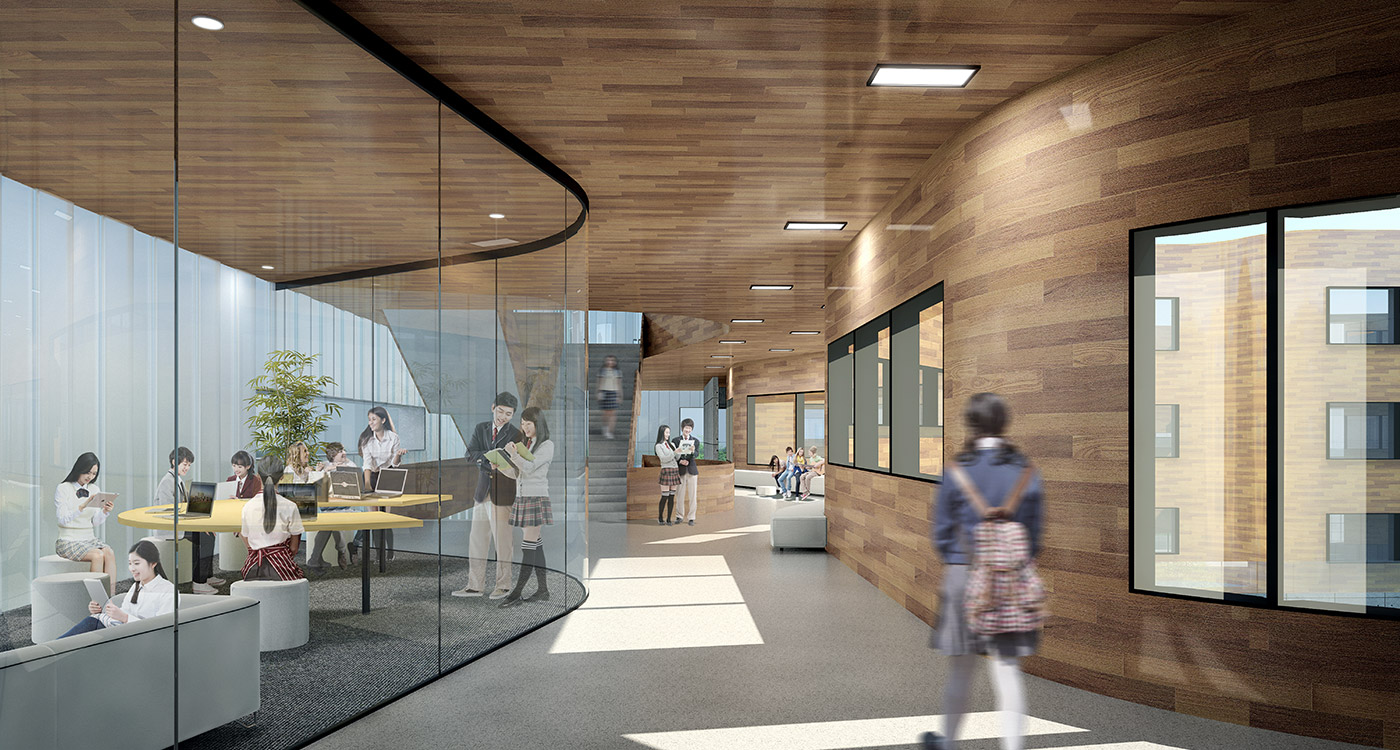
Cutting edge education models explore a more interactive, collaborative, inquisitive, student-centred, teaching-learning environment. Consequently the goal of the contemporary school building is to blur the line between formal teaching in classrooms and the informal learning of the in-between spaces. With smart spatial design, informal teaching can inhabit the informal learning spaces, and vice versa. This new approach to education requires the entire school to become a teaching-learning environment.
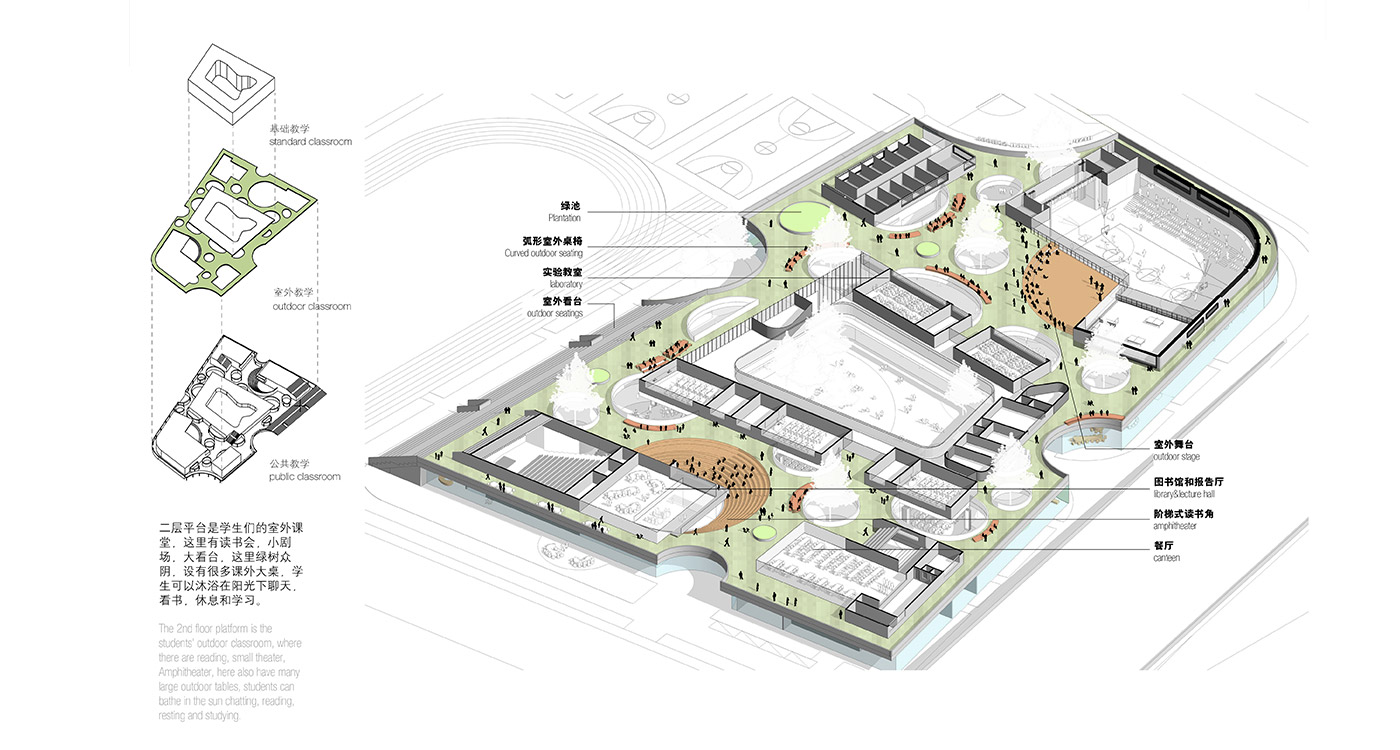
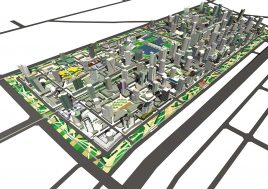
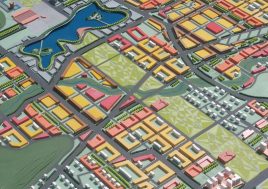
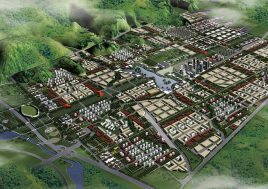
artificial plateau
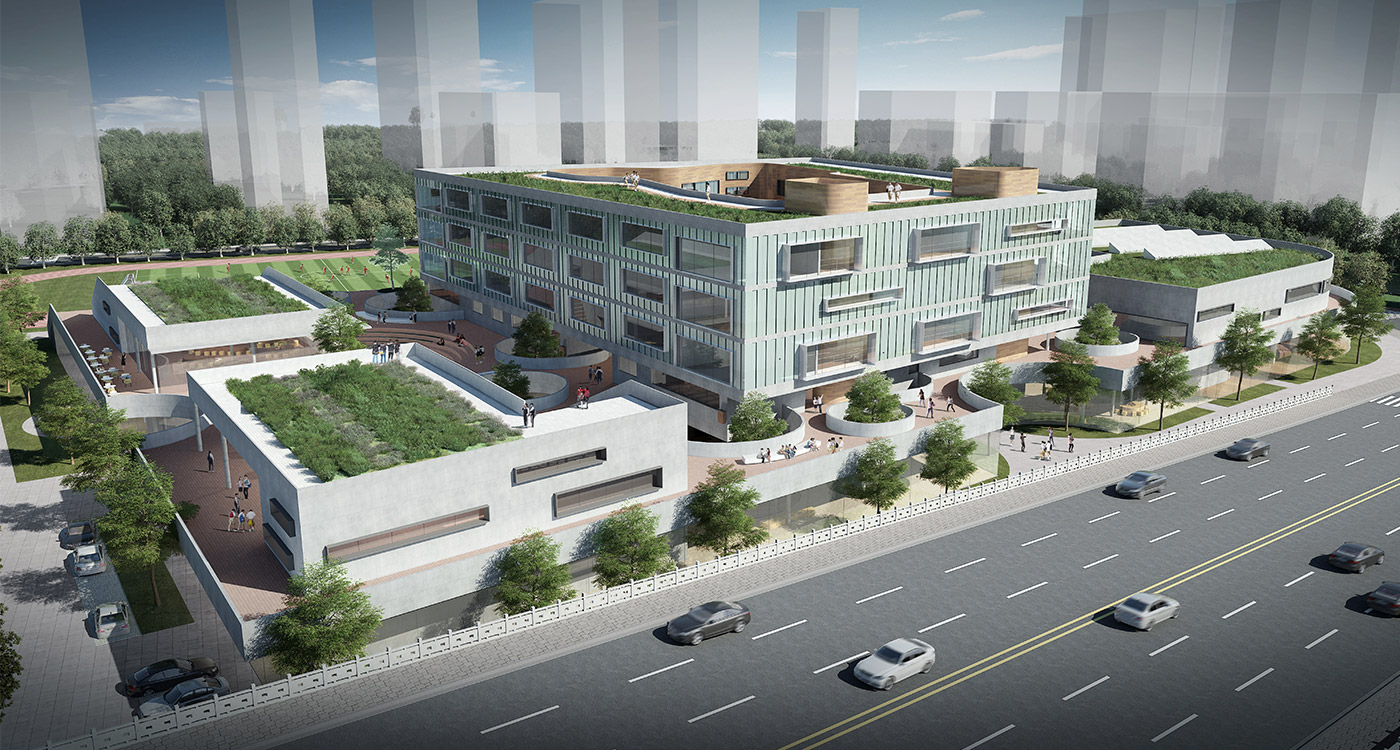
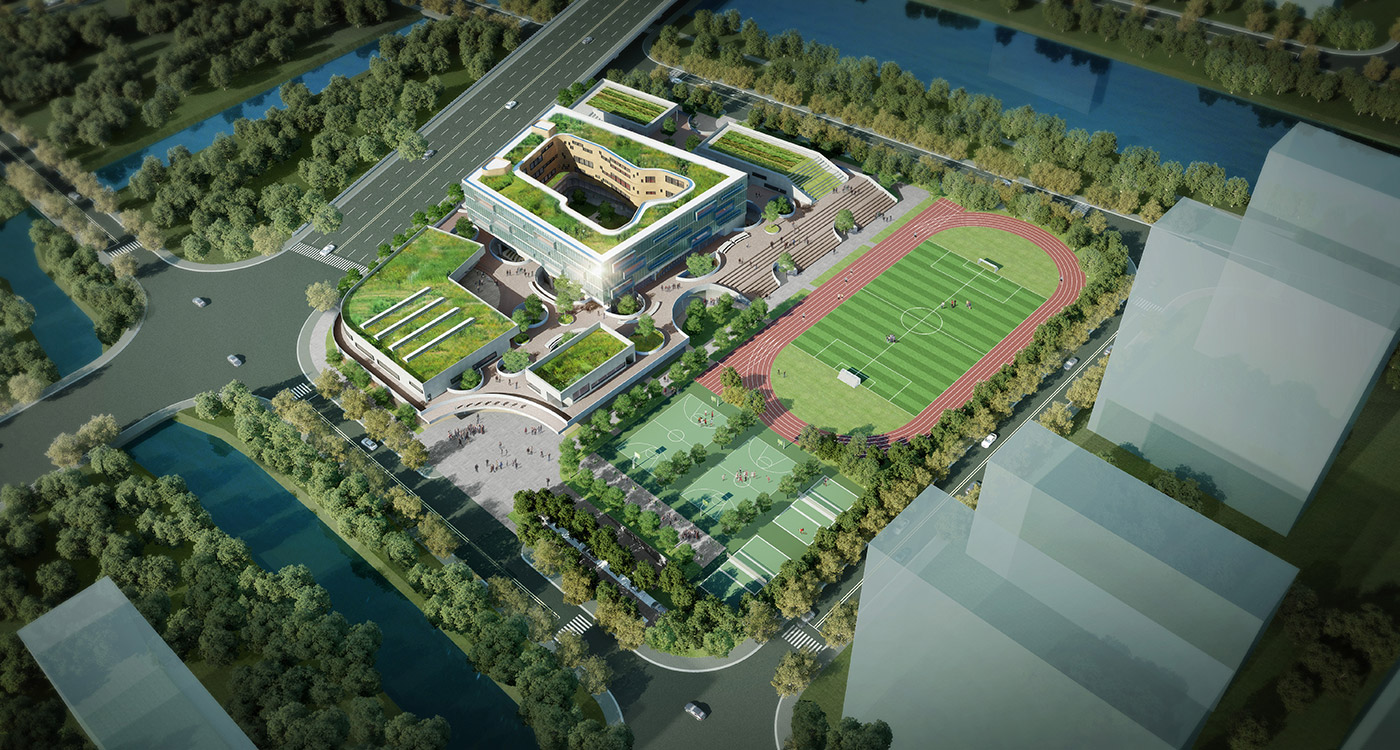
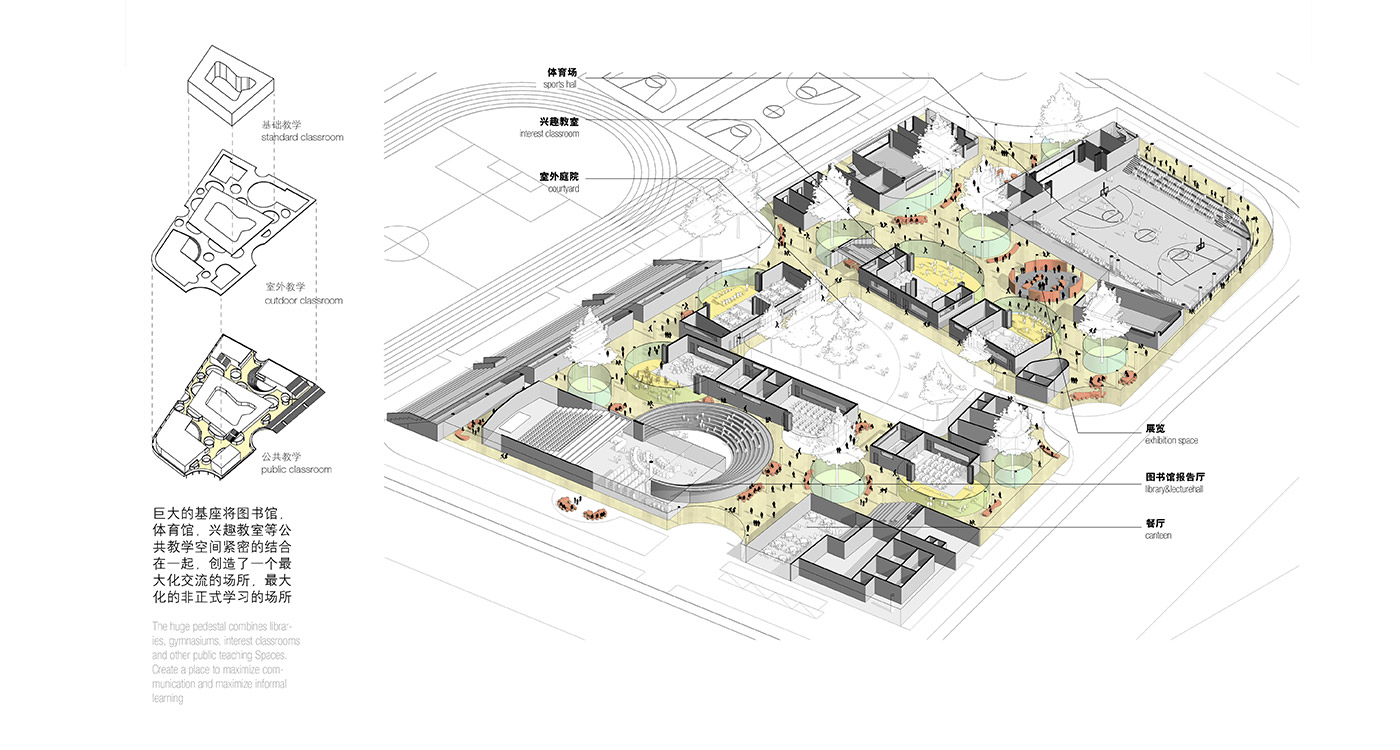
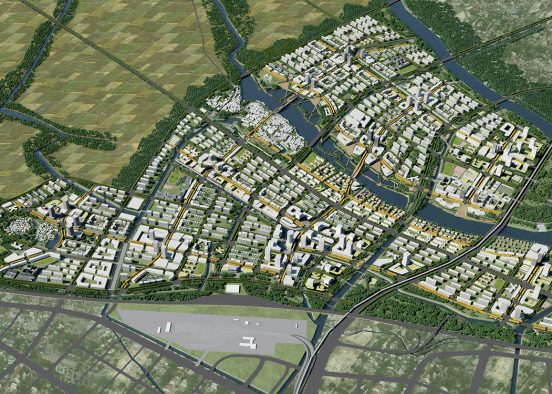
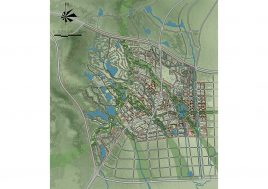
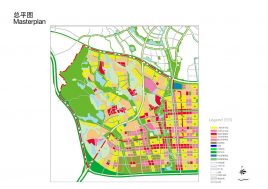
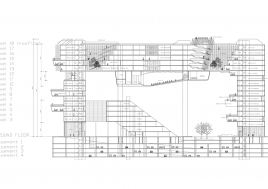
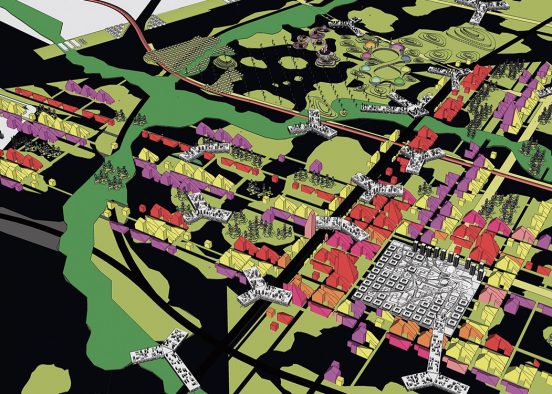
It is not unusual in China for school sites to be very tight for the space required for the program requirements, with the areas for ground floor programs (communal areas, specialized teaching facilities, administration, and sports fields) close to or exceeding the site area.
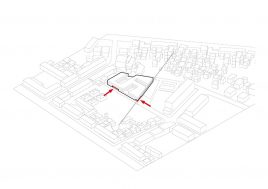
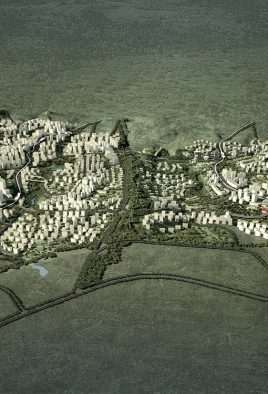
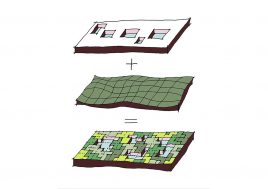
This project explores the idea of building an artificial plateau or terrace covering half the site, in effect providing one and a half sites. This terrace provides two ground floors on which to distribute the ground floor requirements of the brief.
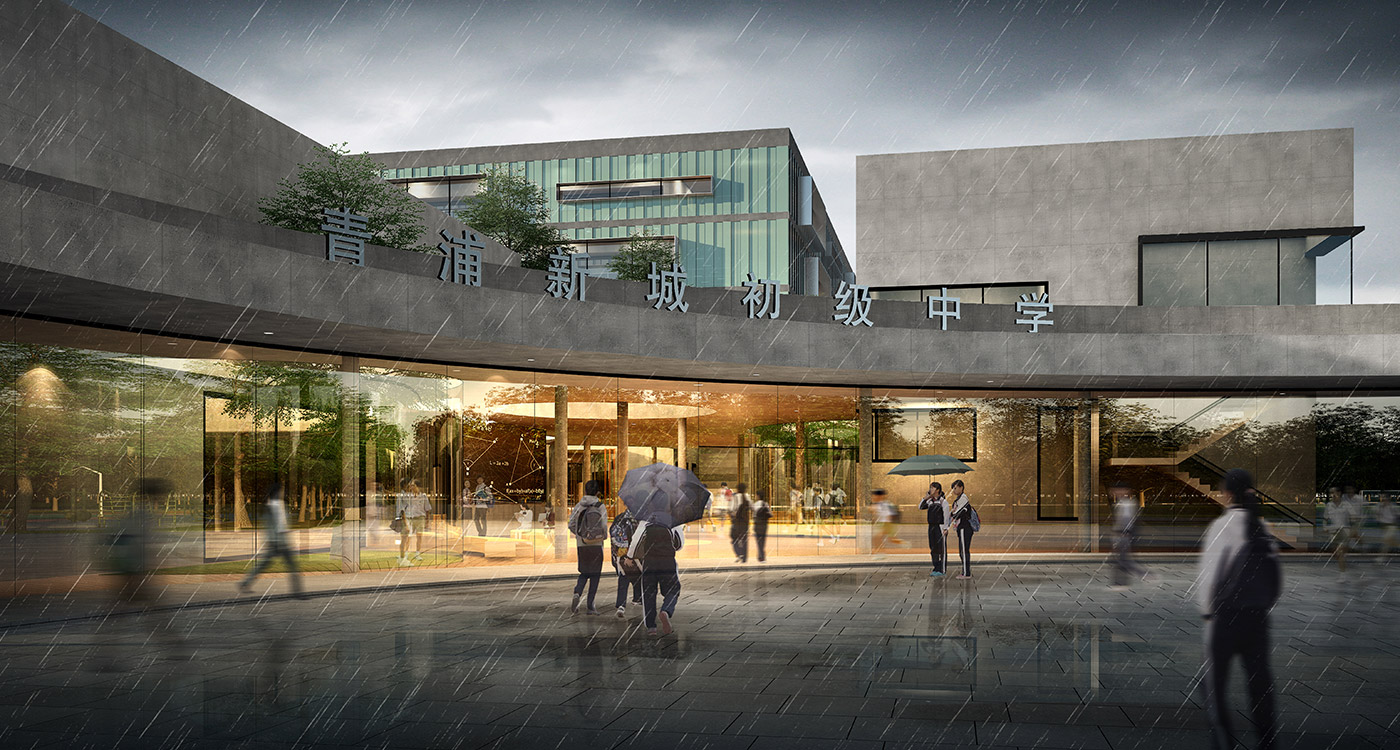
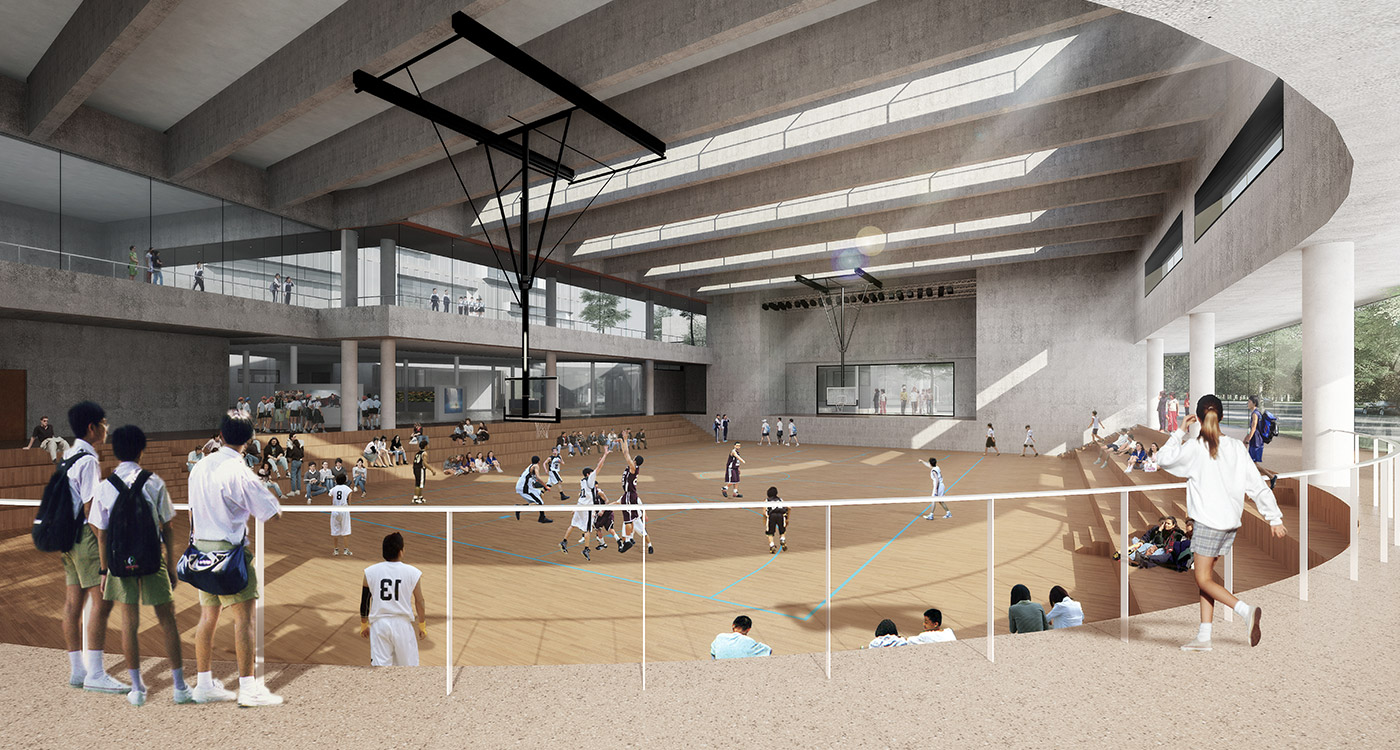
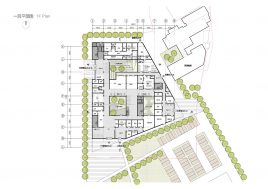
Communal facilities (sports hall, canteen, exhibition space, specialist classrooms, library and large lecture hall) are on the first ground floor under terrace. These facilities are linked by a clear and legible circulation space that explores informal teaching and learning opportunities.
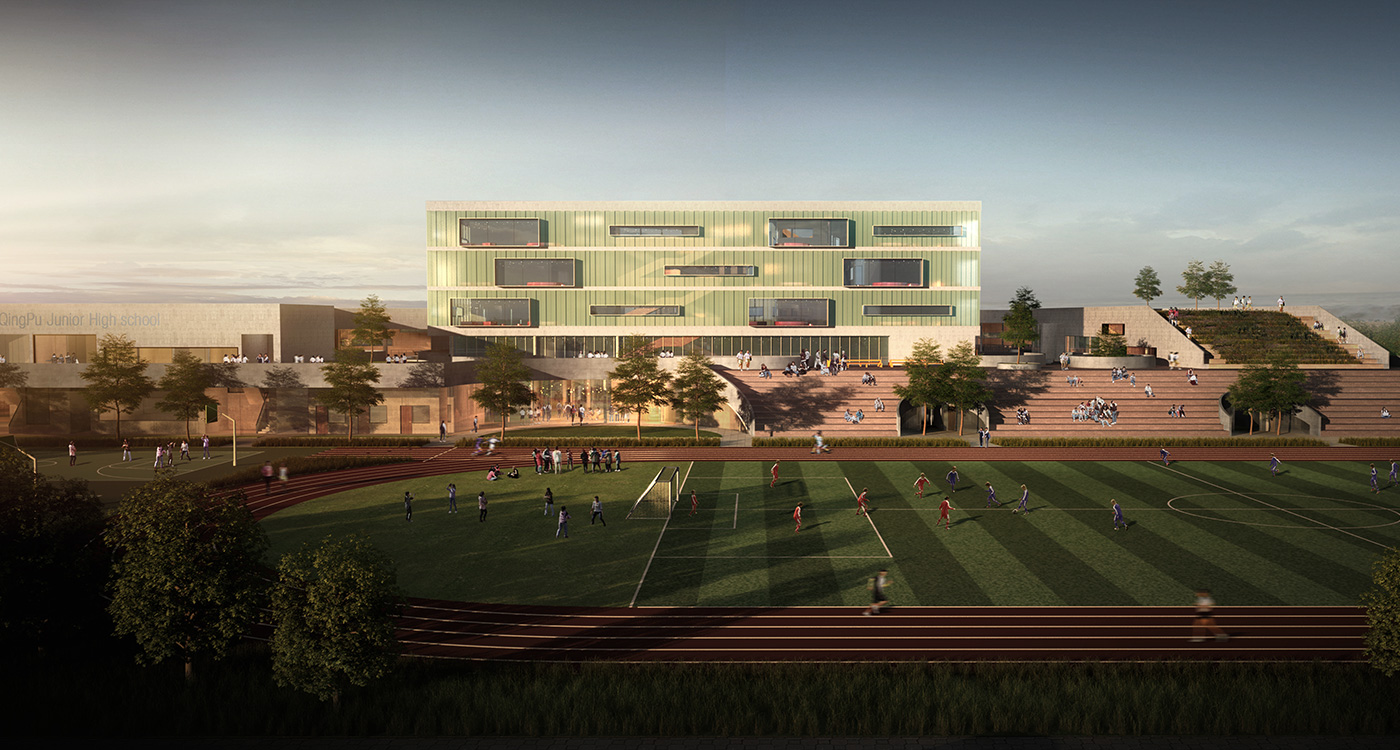
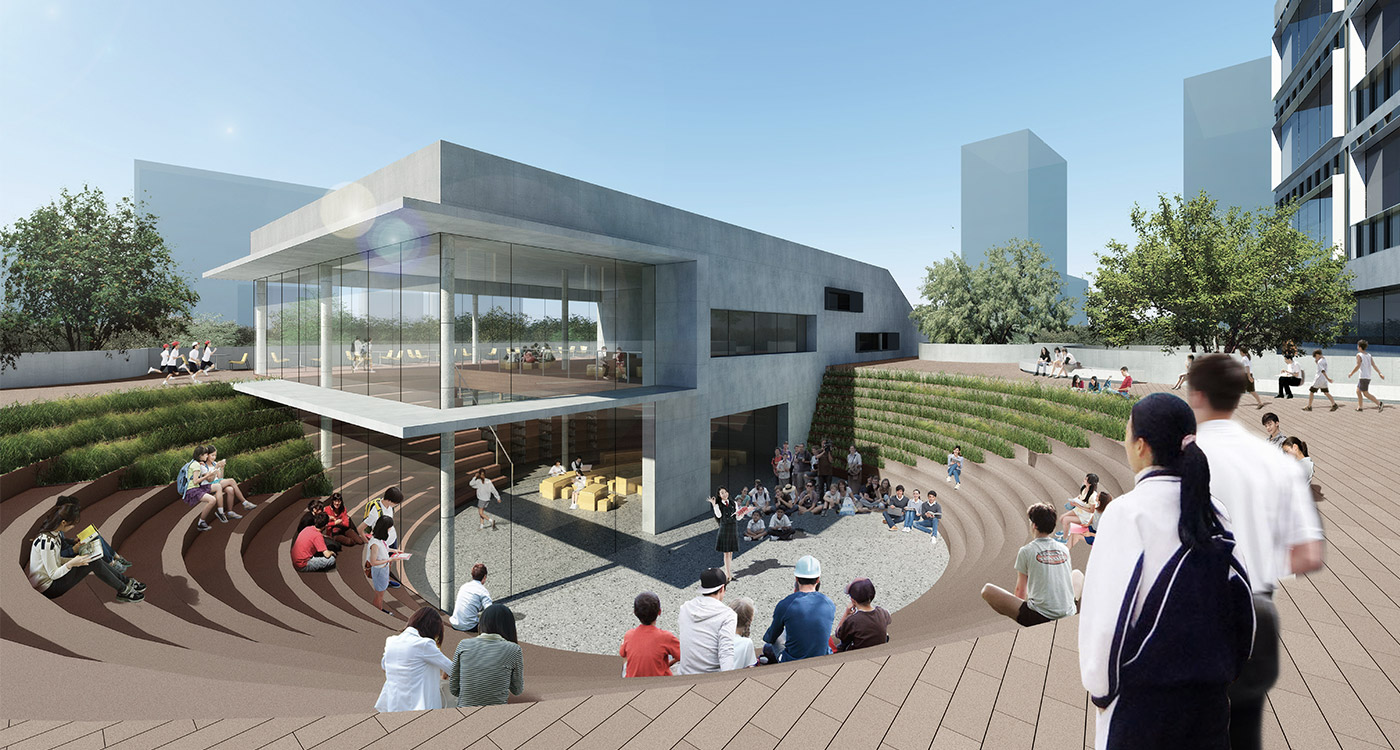
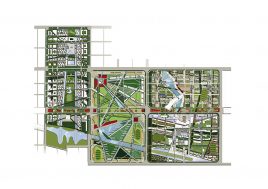
the terrace
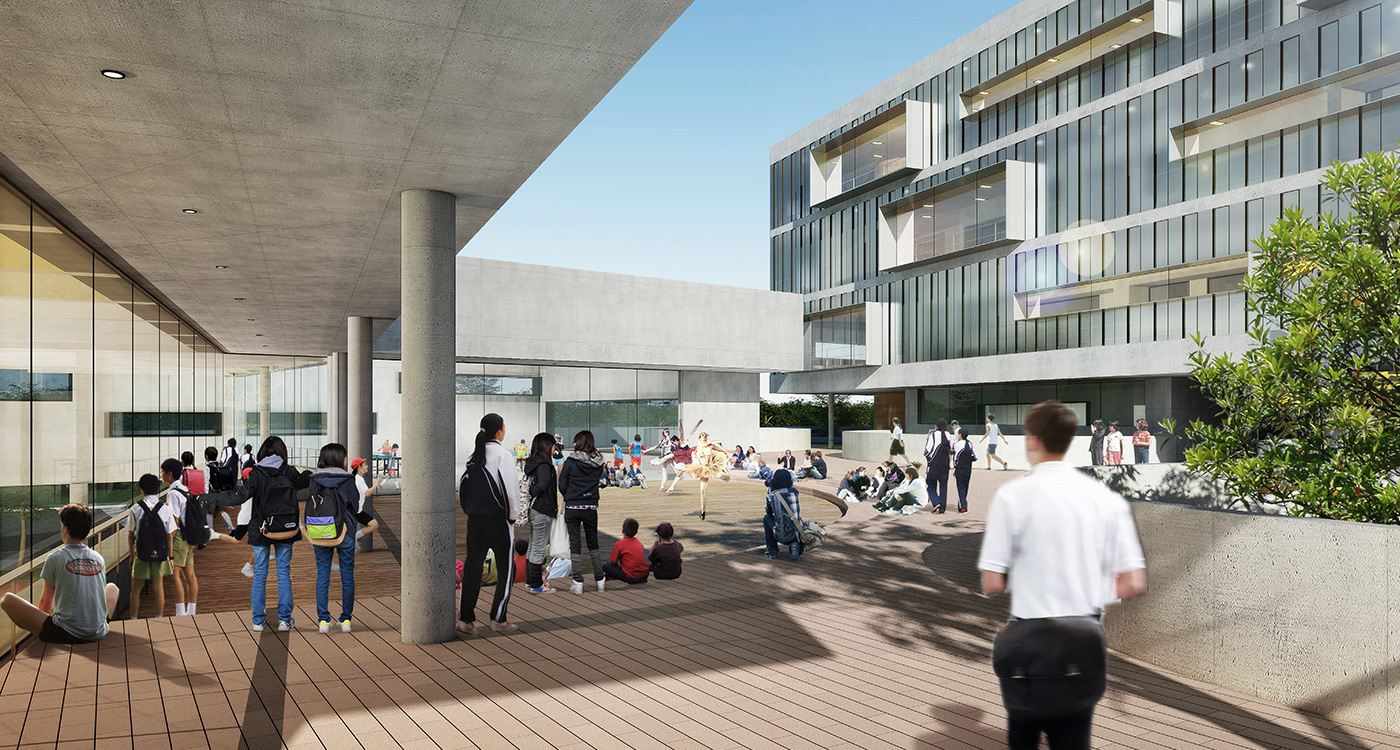
The terrace level is seen as one large informal outdoor teaching and learning space. It is punctured by a large central courtyard and a number of smaller courts to provide light and ventilation to the programs below. The edge between the terrace level and the sports grounds is a multi level, multi-use space, forming a generous amphitheatre from which to view the sports grounds and is a great place for the students to hang out and relax. The canteen and the library are also directly accessible from the terrace.
The terrace is also the site for five function-driven buildings, which accommodate further communal programs at terrace level. The largest building contains standard classrooms at the upper levels that are linked by an internal peer-to-peer learning circuit, which is wrapped around the large central courtyard in the terrace, visually linking all classrooms through to the ground floor programs.
generosity
Due to the artificial plateau, even a tight site with a big program can have the generosity to explore contemporary teaching and learning environments.
- Infrastructure
- Public
- Residential
- Healthcare
- Education
- Culture
- Office
- Retail
- Hotel
- Hospitality
- Mixed Use
- Sports
- Planning
- Urban Design
- Public Landscapes
- Private Landscapes
- Playgrounds
- Structures & Pavillions
- Residential
- Healthcare
- Education
- Culture
- Office
- Retail
- Hotel
- Hospitality
- 2023
- 2024
- 2021
- 2020
- 2019
- 2018
- 2017
- 2016
- 2015
- 2014
- 2013
- 2012
- 2011
- 2005-2010
- 2000-2005
- 1990-2000

























































































































































































































































































































































 Back to projects
Back to projects